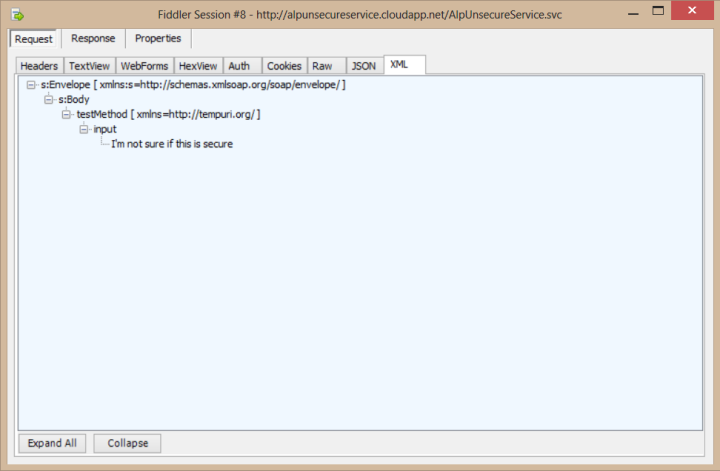
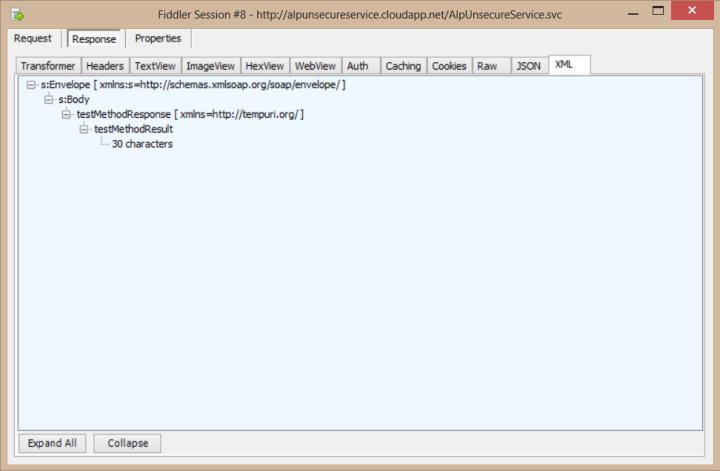
One of the most prominent features of Windows Azure is no doubt Windows Azure SQL Databases, which allows us to have a database on the cloud and benefit from the advantages of cloud computing, such as high-availability and scalability. Azure’s portal interface allows us to easily manage the database, and by using a cloud service as an API for our backend we can quickly access the database from any platform.
In this step by step article, we’ll create a Windows Azure SQL Database, create a web service which connects to this database and allows us to perform specific operations on it and then use that web service in a Windows Store app.
1) Creating the Windows Azure SQL Database
Obviously, you’ll need to have an Azure account to do this. You can go to http://www.windowsazure.com and click on the Free Trial option on the upper right and follow the instructions to get a free 1 month trial. Keep in mind that although it is free, you still need to enter a valid credit card information for validation purposes.
After you get an Azure account (or if you already have one), click “Portal” on the upper right or go to http://manage.windowsazure.com and log into the Management Portal.